Position in CSS
Detailed guide of Static, Relative, Absolute, Fixed and Sticky positions in CSS

The position property of CSS is used for positioning an element in the document. We have five different position values and after selecting any position value we can finally determine its location using top, right, bottom and left values.
Now let discuss what are this position values and how they functions in the document.
1. position: static;
Static is the default position in html. We cant change the location of an element using top, right, bottom or left values when the position is static or default. It is positioned according to the normal flow of document.
2. position: relative;
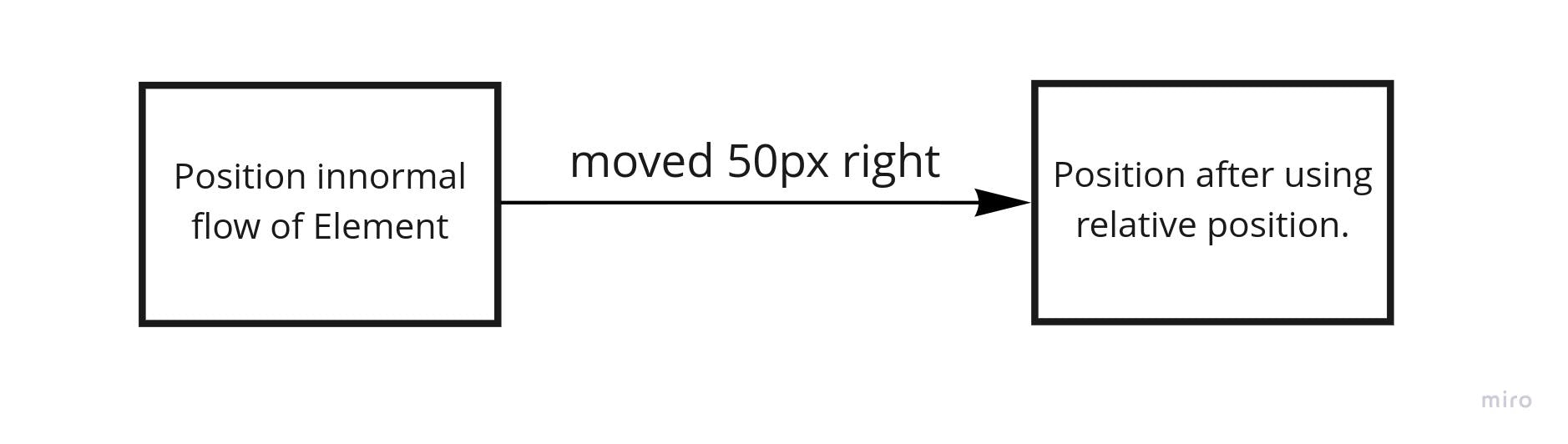
The element with relative position is positioned according to the normal flow of the document but we can change its location by mentioning the direction values of top, right, bottom and left. It will move according to its direction values from its previous position.
Example:
{
position: relative;
right: 50px;
}
Output:
3. position: absolute;
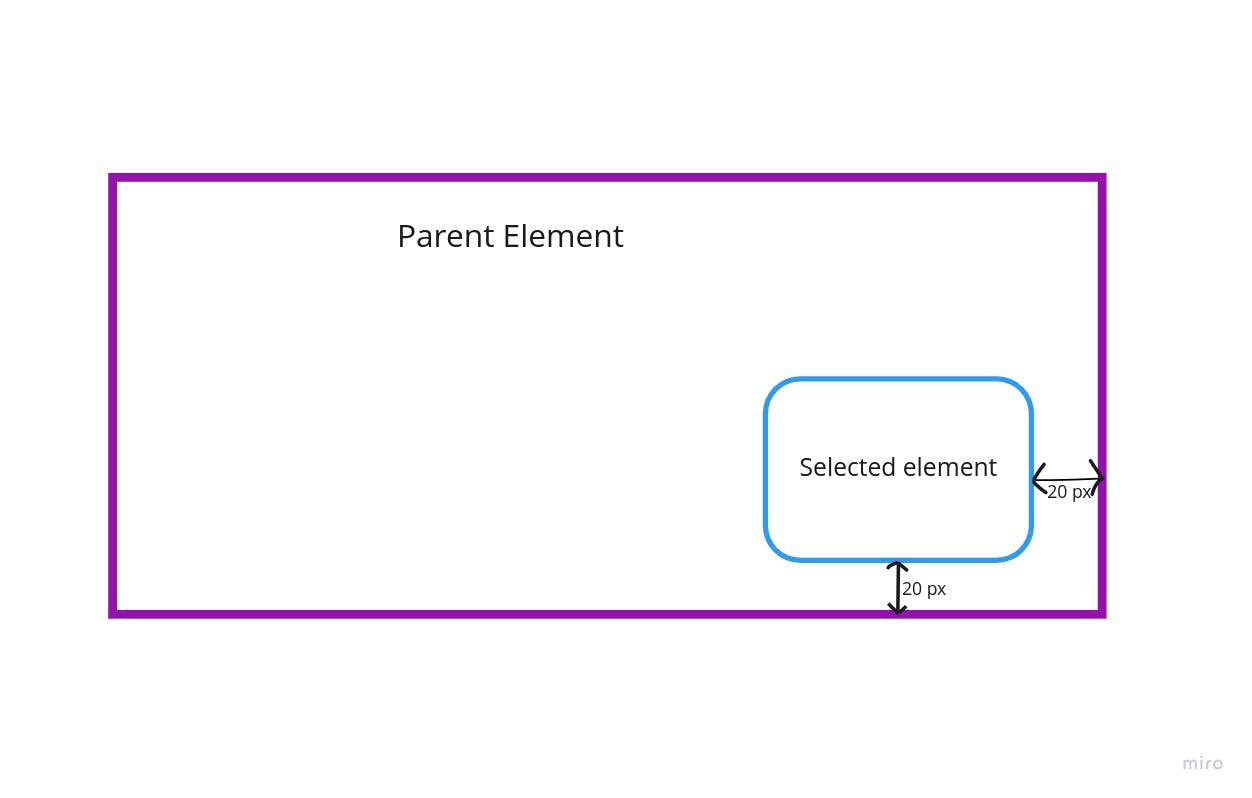
When the position value is set to absolute, it is removed from its normal document flow and no space is allotted for the element. It is now positioned relative to its parent element. We can now move this element from its parent element or initial containing block by setting top, right, bottom and left values.
Example:
{
position: absolute;
right: 20px;
bottom: 20px;
}
Output:
4. position: fixed;
In the fixed position, the element is removed from its normal flow of the document and it is now positioned in a particular position relative to the viewport of the page regardless of scrolling. That means the position will be unchanged on the screen while the user is scrolling on the page. Though the position of the element can be changed using top, right, bottom, and left values.
Example:
footer{
position: fixed;
bottom: 0px;
}
Output:

5. position: sticky;
The fixed and sticky positions work almost similarly but there is a small difference between them. In the case of fixed position, the position of the element does not change during the time of scrolling, but in the case of sticky the position of the element is changed during the time of scrolling but it never leaves the viewport area (screen). The sticky element always sticks to its nearest parent element which has a scrolling mechanism.
Example:
.heading{
position: sticky;
top: 0;
}