Table of contents
Introduction
Linux is an open-source operating system with a diverse range of desktop environments to choose from. A desktop environment is a graphical user interface (GUI) that allows users to interact with the operating system through icons, windows, and menus. Choosing the right desktop environment is important, as it affects the user's experience with the operating system, including ease of use, customizability, and performance. Three of the most popular Linux desktop environments are GNOME, KDE, and Xfce, each with its own unique features and advantages.
GNOME
GNOME, short for GNU Network Object Model Environment, is one of the most popular Linux desktop environments. It was first released in 1999 and has since undergone several iterations and updates. GNOME is designed to be simple, intuitive, and accessible to users of all skill levels.

User interface and design philosophy:
GNOME has a minimalist and streamlined design, with a focus on usability and accessibility. The desktop environment features a top bar that houses the application menu, system status indicators, and other commonly used features. The application windows have a clean and modern look, with a focus on content and functionality rather than aesthetics.
Applications and features:
GNOME comes with a variety of built-in applications, including a web browser, file manager, text editor, and media player. It also has a range of customization options, including the ability to change the theme, icons, and fonts. GNOME is designed to be extensible, with support for a range of plugins and extensions that can enhance the user experience.
Pros and cons of GNOME:
GNOME's minimalist design and ease of use make it an excellent choice for beginners and those who prefer a clean and simple interface. However, some users may find GNOME's lack of customization options, compatibility issues, and resource-intensive nature to be a disadvantage.
KDE
KDE, short for K Desktop Environment, is another popular Linux desktop environment. It was first released in 1996 and has since undergone several major updates and redesigns. KDE is known for its flexibility, customization options, and advanced features.
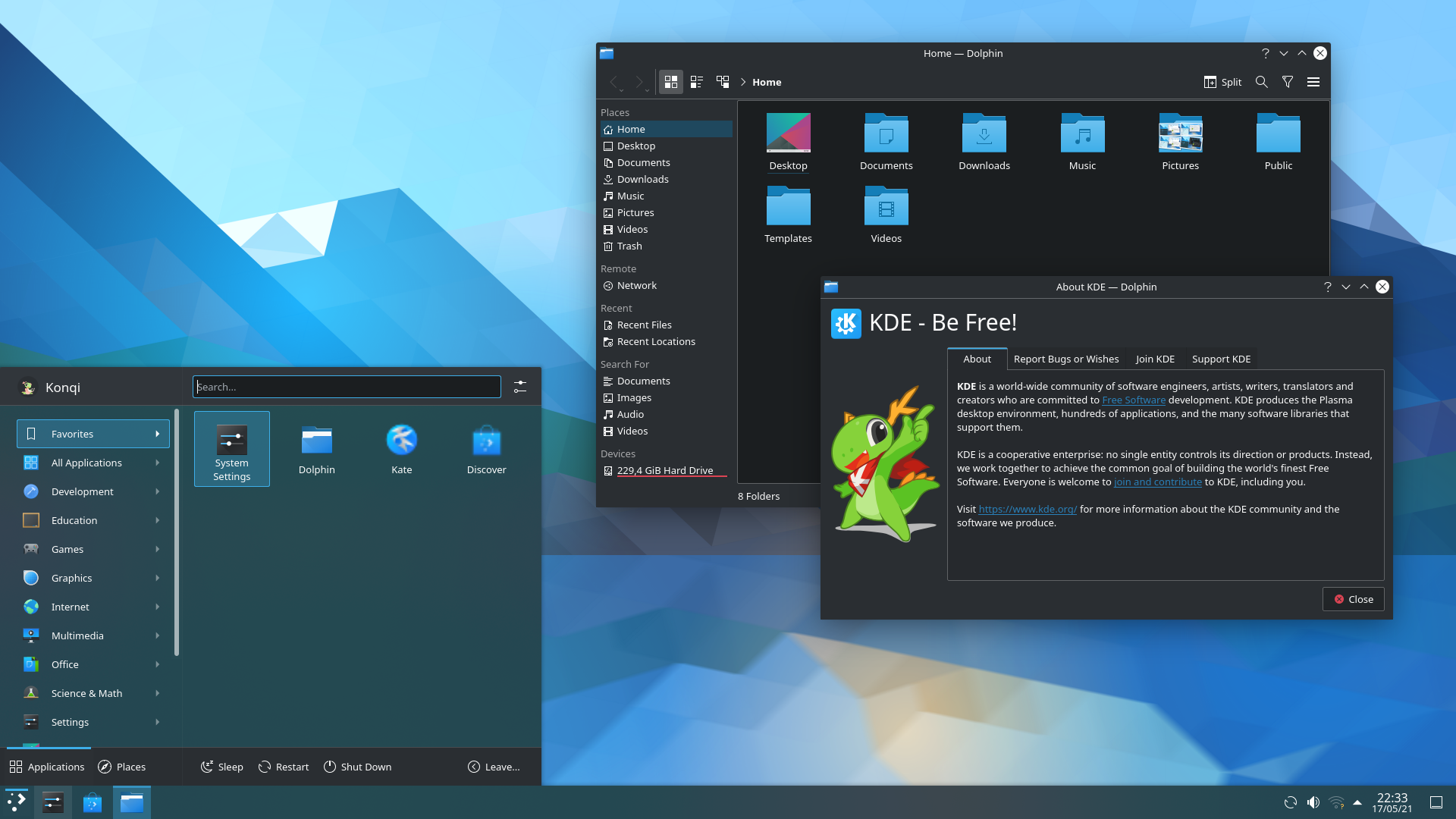
User interface and design philosophy:
KDE has a more complex and feature-rich interface than GNOME. It features a panel that can be customized with a range of widgets and applets, as well as a launcher menu that can be configured to suit the user's preferences. KDE also has a range of window management options, including the ability to create custom desktops and workspaces.
Applications and features:
KDE comes with a wide range of applications, including a web browser, email client, file manager, and media player. It also has a range of advanced features, such as support for multiple desktops, virtual terminals, and powerful window management tools. KDE is highly customizable, with support for a range of themes, widgets, and extensions. KDE also comes with a cross-platform application called 'KDE Connect' that allows users to share files, notifications, and media between their mobile devices and desktop computers. It also provides remote control functionality for media playback and other tasks.
Pros and cons of KDE:
KDE's advanced features and customization options make it an excellent choice for power users and those who require a high degree of flexibility. However, some users may find KDE's complex interface and resource-intensive nature to be overwhelming or sluggish.
Xfce
Xfce is a lightweight Linux desktop environment that is designed to be fast and efficient. It was first released in 1996 and has since undergone several major updates and redesigns. Xfce is known for its low system requirements and excellent performance on older hardware.
![xfce:getting-started [Xfce Docs]](https://docs.xfce.org/_media/xfce/slider-desktop.jpg?w=600&tok=d15f32)
User interface and design philosophy:
Xfce has a simple and straightforward interface that is designed to be easy to use and understand. It features a traditional desktop layout, with a panel at the bottom of the screen that houses the application menu, system status indicators, and other commonly used features. The application windows have a clean and modern look, with a focus on functionality rather than aesthetics.
Applications and features:
Xfce comes with a range of built-in applications, including a file manager, text editor, web browser, and media player. While Xfce may not have as many built-in applications as GNOME or KDE, it can still run a wide range of Linux applications. Xfce also has a range of customization options, including support for themes, icons, and fonts.
Pros and cons of Xfce:
Xfce's lightweight and efficient nature makes it an excellent choice for users with older hardware or those who require a fast and responsive desktop environment. However, some users may find Xfce's lack of advanced features and customization options to be a disadvantage.
Linux offers a variety of desktop environments to choose from, including GNOME, KDE, and Xfce. Each has its own unique features and advantages. GNOME is easy to use, KDE is highly customizable, and Xfce is lightweight and efficient. When choosing a Linux desktop environment, users should consider factors such as performance, customization options, application availability, ease of use, and security and privacy features.
Comparison of GNOME, KDE, and Xfce
The GNOME, KDE, and Xfce desktop environments are all popular choices for Linux users. While they share some similarities, there are also some key differences between them. Here are some of the main differences:
Performance and resource usage:
GNOME is known for being resource-intensive and can be slow on older hardware. KDE can also be resource-intensive, but it has advanced performance optimization features that can improve performance on older hardware. Xfce is known for being lightweight and efficient, making it an excellent choice for users with older hardware or those who require a fast and responsive desktop environment.
Customization options:
KDE is known for having the most advanced customization options, with support for a range of themes, widgets, and extensions. GNOME also has a range of customization options, but they may not be as extensive as KDE's. Xfce has fewer customization options than GNOME or KDE, but it can still be customized to suit the user's preferences.
Application availability and compatibility:
GNOME and KDE have a wide range of built-in applications and can run most Linux applications. Xfce has fewer built-in applications but can still run a wide range of Linux applications.
Ease of use and user experience:
GNOME and Xfce are known for being easy to use and intuitive, while KDE can be more complex and overwhelming for beginners. However, KDE's advanced features and customization options can make it an excellent choice for power users.
Security and privacy:
All three desktop environments are open-source and have a range of security and privacy features. However, GNOME is known for being particularly privacy-focused, with features such as the Privacy Settings tool that allows users to control their privacy settings and data collection.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the right Linux desktop environment is important for a positive user experience with the operating system. GNOME, KDE, and Xfce are three of the most popular Linux desktop environments, each with its own unique features and advantages. GNOME is known for its minimalist design and ease of use, while KDE is known for its advanced features and customization options. Xfce is known for its lightweight and efficient nature, making it an excellent choice for users with older hardware or those who require a fast and responsive desktop environment.
When choosing a Linux desktop environment, users should consider factors such as performance and resource usage, customization options, application availability and compatibility, ease of use and user experience, and security and privacy features. Ultimately, the choice of desktop environment will depend on the user's preferences and requirements.
Future developments in Linux desktop environments are likely to focus on improving performance and resource usage, enhancing customization options and user experience, and improving security and privacy features. As Linux continues to gain popularity as an operating system, it is likely that we will see continued innovation and development in Linux desktop environments.

